 Ellisinterstellar Logo
Ellisinterstellar Logo Orion Interstellar Travel
Orion Interstellar Travel Black Hole Picture
Black Hole Picture  Ellisinterstellar Logo Ellisinterstellar Logo |
|
 Orion Interstellar Travel Orion Interstellar Travel |
 Black Hole Picture Black Hole Picture |
Welcome * Bienvenida * Accueil * Emplang * Benvenuto * Velkommen * Welkom * Willkommen

A little history is in order here. During the greater than 15 years we have been working on the Decisions Aids project, we have published numerous reports, briefings, and publications. Following is some of our work in that regard.
On May 16, 2002, the authors hosted a workshop entitled Computer Algorithms for Human Decision Making in Colorado Springs, CO with the objective being to provide a technical forum for interested researchers and their customers to exchange ideas on advanced information processing technologies that aid human decision making.
Reports and Briefings:
Publications:
Feb. 20-22, 2002, the Air Force Information Warfare Center (AFIWC) hosted an unclassified workshop entitled Phoenix Challenge 2002 at the New Mexico State University facility in Las Cruces, NM. The authors participated in this workshop by presenting two papers and providing a live demonstration at a Phoenix Challenge booth. The papers are available here:
September 13-16, 2012, the 100 Year Starship (100YSS) project hosted an unclassified public symposium entitled 100 Year Starship - Canopus 310 LY in Houston, TX. The authors participated in this workshop by presenting a paper in the Time and Distance Solutions track entitled Transition from Niche Decision Support to Pervasive Cybernetics by Patrick J. Talbot, Patrick Talbot Consulting.
October 28-31, 2015, the 100 Year Starship
(100YSS) project hosted an unclassified public symposium entitled 100
Year Starship - Canopus 310 LY - Finding Planet Earth 2.0 in Santa Clara, CA. The authors
participated in this workshop by presenting a paper entitled Goldilocks Zones - A
Fine-Grained Exoplanet Taxonomy by Patrick J. Talbot, Patrick Talbot Consulting.
The 100YSS Powerpoint presentation.
The 100YSS proceedings paper.
To learn more about Exoplanets, visit the following sites:

Sites of Interest:


Books of Interest:

The Decision Aids toolkit is the product of multiple years of research and prototype development under the auspices of several Internal Research & Development (IR&D) projects. The Decision Aids toolkit has primarily focused on the following broad concepts:
Over the years, various algorithms and tools have been implemented and tailored to apply to new and evolving technology. The Decision Aids toolkit is hosted on a PC based Windows platform running Java in order to support better platform interoperability. The key Decision Aids capabilities described here include:
The Decision Support Aids are applicable to many types of decisions and, over a period of years, the Decision Aids toolkit suite has been tailored to address many domains and specific scenarios. Examples of supported mission domains to which algorithms have been applied include: Space Control, Strategic Forces, Missile Defense, Air Operations, Homeland Defense, Intelligence Analysis and Information Operations (IO). This flexible Decision Support Tools characteristic has enabled them to be tailored and streamlined to be an effective key player in supporting numerous domains.
Decision-makers are busier than ever and clamor for automated help. We are pioneers in the application of artificial intelligence to decision making with the following innovations:
Decision-making requires that data be filtered and refined to provide information. Adding context to the content produces actionable knowledge. Unfortunately, current techniques strip away the uncertainty associated with raw data. Our design provides a decision-centered approach for coping with uncertainty that combines what people do best with what computers do best. Algorithms use a knowledge base from a single import/export interface, facilitating multi-strategy reasoning. Triage filters the data, extraction of hedge words captures uncertainty, an executable knowledge base provides content in context, data fusion propagates uncertainty, data analytics discover patterns, and plan optimization tools move the decision-making from 'what's going on' to 'what to do'. Displays present actionable knowledge with associated uncertainties explicitly shown.
During the course of our investigations, we have evaluated numerous software packages and integrated systems that can be used for decision support. The following lists some of these tools. Some of these tools are used in the Decision Support Aids toolbox and others were evaluated for their future usefulness but were never officially used or incorporated into the Decision Support Aids toolbox described here. To see a list of these and their functionality, click here.
The figure below shows the architecture of the software implementation of our current testbed.
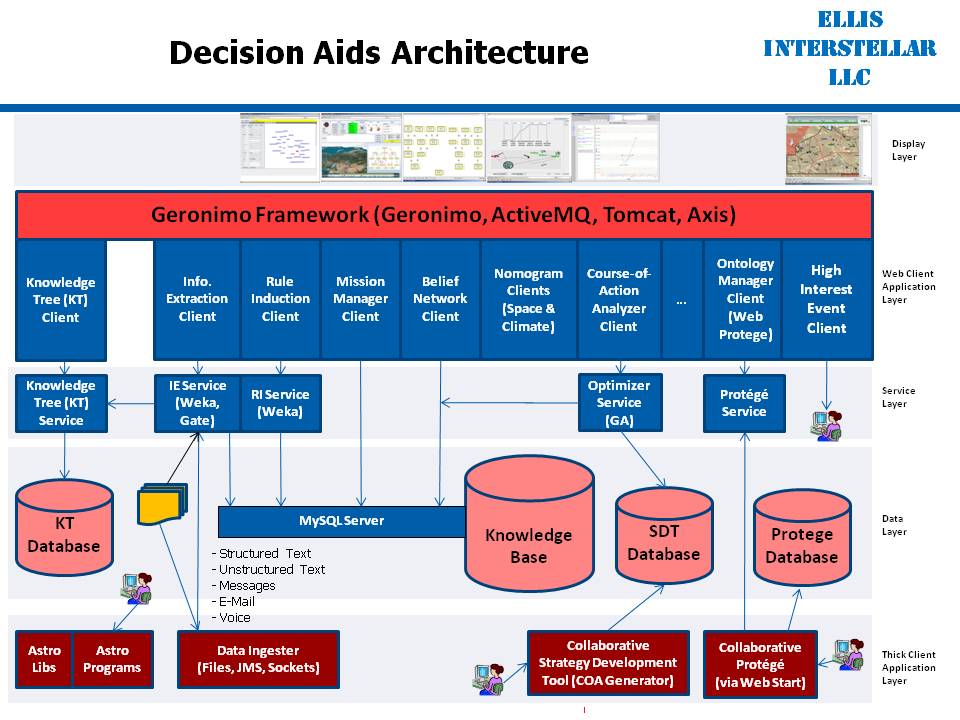
Knowledge Tree document management system
The KnowledgeTree functional element is an open source document
management system which seamlessly connects people, ideas, and
processes to satisfy all your collaboration, compliance, and
business process requirements. KnowledgeTree works with Microsoft
Office, Microsoft Windows and Linux. KnowledgeTree securely stores,
tracks, organizes, and retrieves all your documents to promote
productivity, collaboration and compliance amongst geographically
dispersed teams. KnowledgeTree solves:
Information Extraction
The Information Extraction (IE) functional element is a name for a top
level service that performs three functions main functions: 1) extract contextual
information from the document, 2) associate the document, and 3) save this information
to a Knowledge Base (KB). The unstructured text is any textual
file (e-mail, news article, memo, presentation, etc) that contains
evidence. The file(s) serves as the input to the entire process. GATE is an open-source
package, which combines some of the most popular text data-mining
tools into one complete package. The majority of the work in this service is done using
GATE. Finally, the classifier tool is Autoclass (a Bayesian
classifier). However, other classifiers such as expert rules, semantic distance, or
operator 'tagging' of a text segment with a hypothesis have been prototyped.
Rule Induction
The Rule Induction (RI) functional element is an
area of machine learning in which formal rules are extracted from a
set of observations. The rules extracted may represent a full
scientific model of the data, or merely represent local patterns in the data. It
is comprised of a GUI, a Rules Induction Service, and supporting
services. The Rule Induction service replicates Quinlan's C4.5 algorithm to produce an
inductive rules tree. The rendering/visualization of the rules tree is conducted using a
browser-based GUI.
Mission Manager
The Mission Manager (MM) functional element is a graphical user
interface (GUI) that provides a way to access other GUIs and
associated command and control applications for analysis services. It closely emulates the
Protégé 3.0 knowledge base version of a previous version of the
Mission Manager. The Mission Manager can be customized so that only the desired
components are provided. The Mission Manager also allows the analyst to use a default Mission
Manager configuration and to load a previously saved configuration.
Belief Network Editor
The Belief Network Editor (BNE) functional element provides evidential reasoning
capability. The theory of belief functions, also referred to as evidence theory or
Dempster Shafer theory (DST), is a well established general framework for reasoning
with uncertainty, with understood connections to other frameworks
such as probability, possibility and imprecise probability theories.
First introduced by Arthur P. Dempster in the context of statistical
inference, the theory was later developed by Glenn Shafer into a
general framework for modeling epistemic uncertainty - a
mathematical theory of evidence. The theory allows one to combine
evidence from different sources and arrive at a degree of belief
(represented by a mathematical object called a belief function) that
takes into account all the available evidence.
Nomograms
The Nomogram (also called a nomograph, alignment chart or abaque)
functional element is a graphical calculating device - a two-dimensional
diagram designed to allow the approximate graphical computation of a
function.
Course-of-Action Analyzer
During the planning process, many decisions must be made with incomplete,
imprecise, and sometimes conflicting goals. Interdependencies among
decisions cause further complications. The COA Analyzer (CA)
functional element makes visible the plan objective, the
interactions available to the planner, the history of interactions
that have shaped the plan, and the library of on-the-shelf plan
options used to construct the plan. It also shows quantitatively the
components of the plan and its predicted effectiveness. As a result, the planner
gains full control of the planning process and results.
Protege Ontology Manager
The Protege functional element is a free open-source ontology editor and
framework for building intelligent systems. Protégé's
plug-in architecture can be adapted to build both simple and complex
ontology-based applications. Developers can integrate the output of
Protégé with rule systems or other problem solvers to construct a wide
range of intelligent systems.
High Interest Event
The High Interest Event (HIE) functional element shows icons that are placed
over a map with geospatial accuracy that represent the following attributes:
Simulated Commander
The Simulated Commander (SC)
functional element provides software control of the Decision Aids
without the need to provide a human-in-the loop. It is provided for
the case where the mission is unmanned and real-time decisions must
continue to be made. By design, the Decision Aids do not initiate any actions.
That function is left to the mission commander. Since on unmanned missions there
is no "commander", one is needed - hence, the Simulated Commander.
To see more information regarding the Simulated Commander,
click here

To see resume, click here
Patrick Talbot was the Chief Technologist for the Northrop Grumman Space Systems Organization when he retired in 2011. His 40 years of experience focused on military command-and-control, climate change, computer network defense, and intelligence community applications, leading to six patents and software solutions for multistrategy reasoning under uncertainty. In the last few years, Patrick Talbot has received several cash awards in idea generation contests sponsored by TopCoder and Innocentive.
Areas of Interest:
To see information regarding our recent research projects,
click here
Disclaimer:
While the author has used good faith efforts to ensure that the information and instructions contained in this work are accurate, the author disclaims all responsibility for errors or omissions, including, without limitation, responsibilty for damages resulting from the use of or reliance on this work. Use of the information and instructions contained in this work is at your own risk. If any code samples or other technology this works contains or describes is subject to open source licenses or intellectual property rights of others, it is your responsibility to ensure that your use thereof compliles with such licenses and/or rights.







